Nigeria Healthtech Ecosystem
Squord Monthly Industry Report
Healthcare technology “healthtech,” refers to startups that use technologies developed for the purpose of improving different aspects of the healthcare system.
In Nigeria, healthtech has been on the rise with a few startups in that space gaining traction and receiving significant funding from investors.
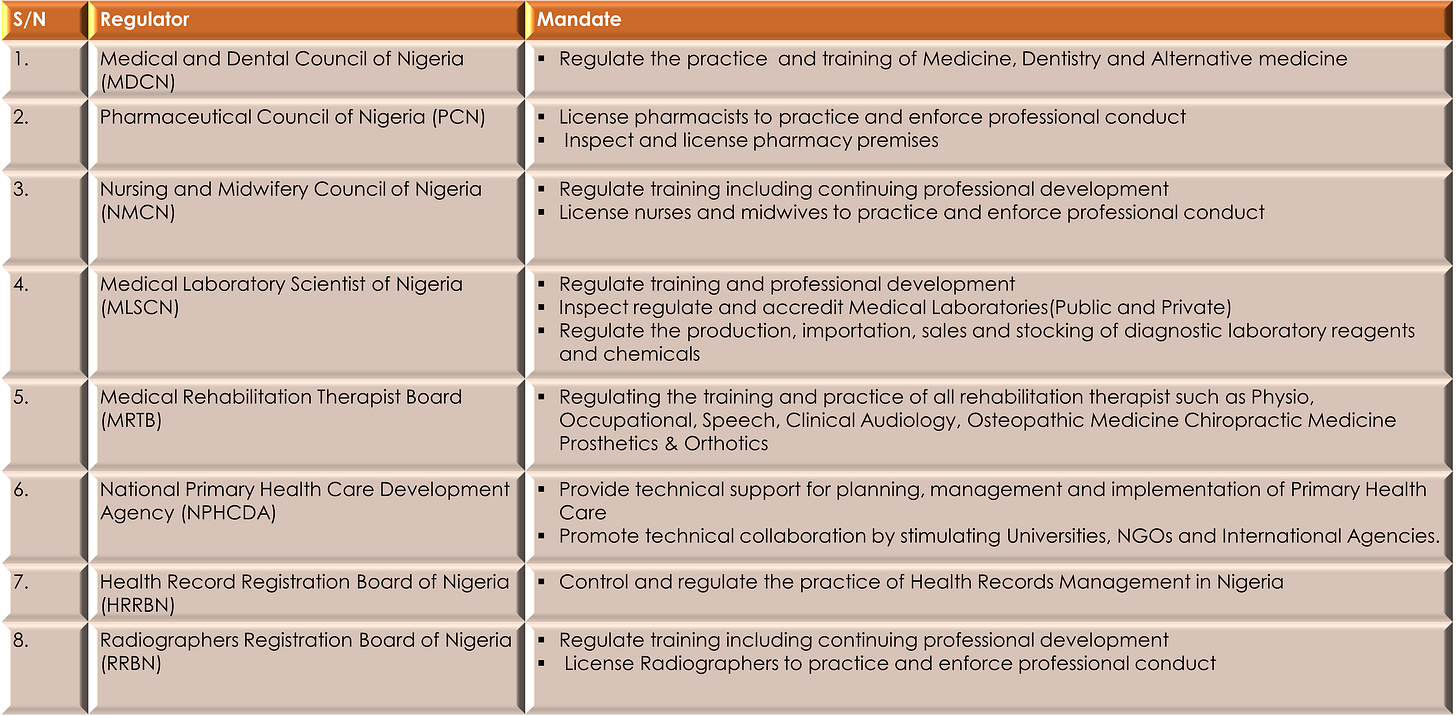
Recently, the Pharmacists Council of Nigeria (PCN) issued the Online Pharmacy Regulations (the Regulations) which regulates pharmacies that use online platforms and mobile apps to deliver their services.
With the pandemic and its associated developments, the ability to quickly and efficiently place orders for drugs and medicine to meet the needs of patients and consumers has become crucial and online-based pharmaceutical service providers have created a niche for themselves by filling this yearning gap.
However, with the increase of these internet-based pharmaceutical service providers, it became necessary to regulate their activities.
In exercise of its powers, the Pharmacists Council of Nigeria (“PCN”) released the Online Pharmacy Regulations ( “the Regulations”), 2021.
Technology has transformed several industries in recent times. The advent of innovative and modern technological advancements has made a notable difference in the medical field. The Regulations are a welcome development as they will serve as a check to the budding market of Providers.
Regulatory Environment
Recent Developments
Launch of E-NHIS
Digitization of Nigeria Health Care System via the inauguration of the E-NHIS system, in accordance with National Health ICT vision.
Enable National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) and other public stakeholders to manage patient claims and payments.
Establishment of Health Infrastructure Bank
Passage of bill by the legislature for the development of Nigeria Health Infrastructure Development Bank.
To provide single digital capital for the development of hospital and referral clinics.
Provision of Fiscal Stance
Introduction of N100bn Healthcare Intervention fund at low interest rates.
Establishment of Health Sector Research and Development Intervention Scheme (HSRDIS).
To strengthen research and development of new and improved drugs, vaccines and diagnostics.
Removal of Bottlenecks
Reduction of registration approval time for operators engaged in critical medical devices needed to contain the pandemic and increase access to the market. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as gloves, protective goggles, face shields, protective gowns and mask (respirators and surgical) reduced to 10days from 120days.
Development of an Economic Sustainability Programme
Introduction of a one-year bridge plan “Economic Sustainability Plan” (ESP) from the Economic Growth and Recovery Plan (EGRP 2017-2020) to support covid -19 intervention. To be carried out through a special intervention fund by tapping into the existing World Bank facility (REDISSE programme).
Birth of Virtual Health
Emergence and acceptance of virtual healthcare other wise known as “Telemedicine”.
Enabling clinicians and patients to stay connected via video chats, phone calls, texts, and emails during COVID lockdowns and quarantines precluded in-person appoint.
Monitoring and Control
Ban of Mars Remedies PVT Ltd India for manufacturing fake medicines or importing pharmaceutical products into the country. Launch of Pharmaceutical Traceability Strategy.
Inauguration of Health Grant
Introduction of $890 million grant from Global Fund in 2020 to tackle HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis (TB), and malaria.
To strengthen health system programs over an implementation period of three years (2021-2023).
Effect of the Pandemic on Healthtech in Nigeria
Before Covid-19 struck, Nigerian health tech companies were overlooked, rarely making the covers of magazines and remaining mostly unknown to the public.
Companies struggled to attract investment or government partnerships that could help them improve public healthcare delivery.
The healthtech industry raised only $7.8million in investment from 2014 to 2018, according to a TechCabal report. In contrast, fintech companies raised $482million in the past two years alone.
In the wake of the pandemic, Nigerian health tech companies, have proven essential. Being leveraged across the country to preserve the health of those particularly vulnerable to a virus that infected millions of people all over the world.
The Covid 19 Catalyst
The advent of the pandemic made Venture Capital companies turn attention towards startups in the healthtech space. Calling for collaborations with the Nigerian Center for Disease Control (NCDC) in its pandemic response and management.
Startups were challenged to create solutions to disseminate useful information, help the government monitor infection trends, produce essential medical supplies, and support contact tracing.
Contribution of Healthtech Startups in Nigeria
Nigeria’s health care system has gone from being comparable to the rest of the world in the 70s and early 80s, to one of the world’s most underfunded sectors.
On the global healthcare index, Nigeria’s healthcare ranks as one of the five worst in the world. The health industry is in such awful straits that thousands of doctors have moved abroad in search of better working conditions.
But as the sector struggles to cater to the health needs of nearly 200 million people, an innovative technology scene has created a new wave of startups focused on combating challenges in Nigeria’s health sector.
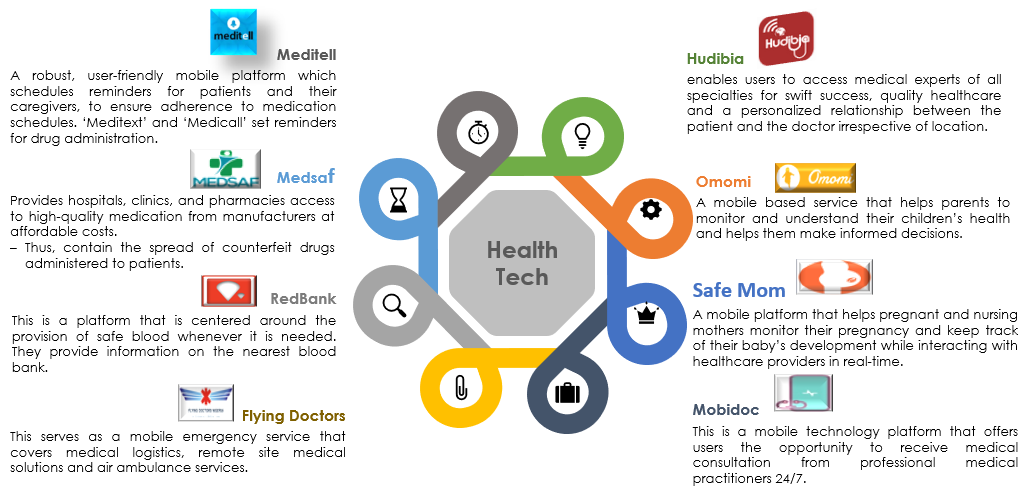
Mumspring provides access to quality perinatal education (antenatal, postnatal, and neonatal) and midwife triage to ensure safe pregnancies, deliveries, and essential after-birth care.
LifeBank is a healthcare technology and logistics company in Lagos, Nigeria. It facilitates the transmission of blood from labs across the country to patients and doctors in hospitals.
Focused on providing access to quality and affordable healthcare for adults and the elderly in Nigeria.
The startup offers a product suite that digitizes data, formalizes monetization and enables telemedicine for health care systems in Nigeria, Liberia, and Ghana.
Provides Genomics data to aid in precision medicine for Africa and the rest of the world. Promoting inclusion in precision medicine through innovative basic, translational, and clinical research.
Others
Some health tech startup funding deals
Opportunities and Challenges in the Health Tech Sector
Opportunities
Socio-economic drivers:
Second largest economy in Africa and the world's seventh largest population exceeding 200 million
Growing middle class
A pro-reform government committed to strengthening the healthcare system
Healthcare policy drivers:
The National Health Insurance Scheme that is expected to improve healthcare services over the long term
The National Health Bill will generate funds and act as a catalyst for health sector improvements; and public private partnerships
Market drivers:
Continuing reliance on imports to supply almost all the market
Digitization of the medical devices import process, which will make it easier to do business in the country
Government moves to introduce a patent regime that complies with the WTO's Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights
Challenges
Soci-economic challenges:
Rising security concerns in northern states
Currency depreciation
Widespread corruption
The autonomy of state governments hindering the implementation of national policies
Financial/funding barriers:
A chronically under-funded healthcare sector with one of the world's lowest levels of per capita health expenditure
Inadequate health budget
Reliance on foreign aid
Slow implementation of universal health insurance; the chaotic management of public healthcare services; a shortage of healthcare personnel in rural areas; and the tendency for wealthier Nigerians to seek medical treatment abroad